Have you ever wondered whether bases are helpful?

Jenn, Founder Calcworkshop®, 15+ Years Experience (Licensed & Certified Teacher)
Understanding the Concept of a Change of Basis
Well, the change of basis, also referred to as the change of coordinate matrix from
As we have discovered, if
Where the scalars
What’s important is that every vector
In particular, our study of isomorphisms showed us how sets of polynomials can “match” elements of
Consequently, by choosing a basis, a vector space of dimension
Why Choose a Different Basis?
I think we can all agree that this is very useful indeed. But what if we want to choose a different basis?
First, let’s talk about why we want to choose a different basis.
From the two images below, which one would be easier to calculate the perimeter and area?
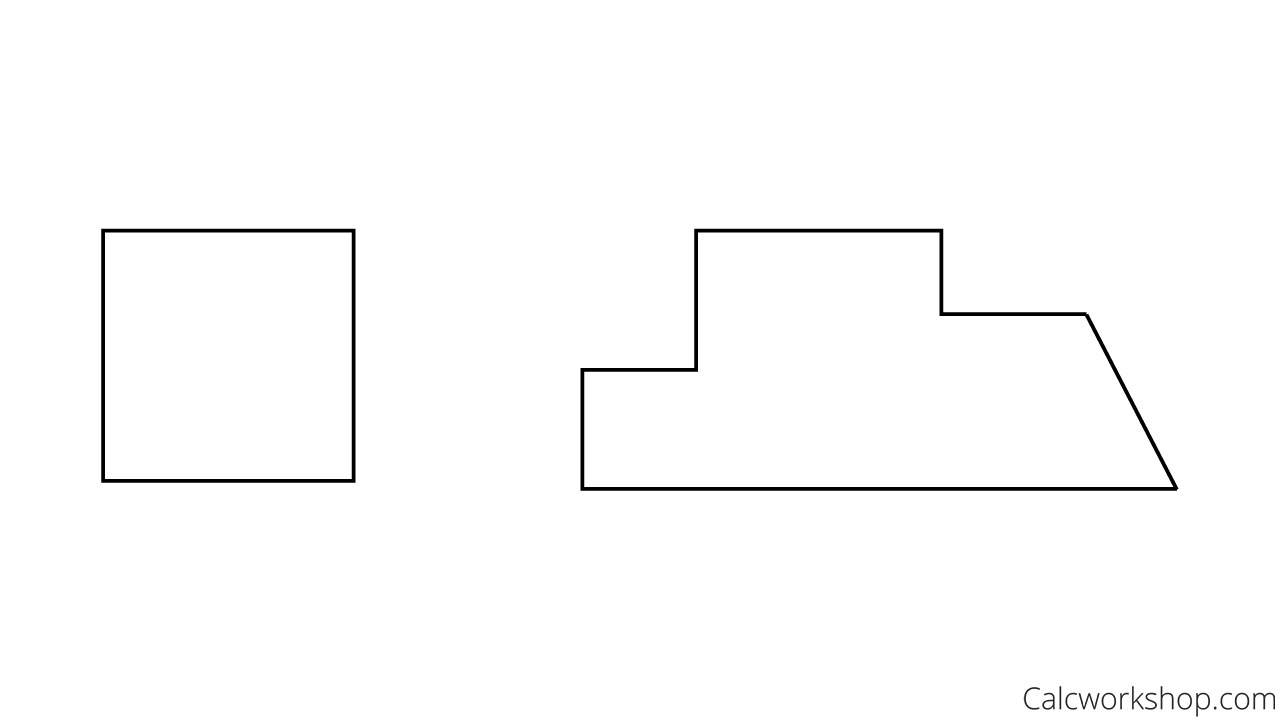
Finding Area – Perimeter (Composite Function)
Indeed, the square on the left is infinitely easier to analyze than the polygon on the right. Choosing the easier of the two shapes is always the most advisable.
Likewise, I think we’d all jump at the chance to work with an easier or more simplified vector space.
And that’s the idea of change of basis. We will change or transform a “hard” basis for one that is “easier.”
Because sometimes we aren’t given a nice “easy” square, but rather something a little unwieldy.
So, if we’re presented initially with a basis B, but the problem’s solution will be significantly aided by changing
And how is this accomplished?
The Mechanics of Change of Basis
If we let
be bases of a vector space
Then there is a unique
Where the columns of
Therefore,
by the invertible matrix theorem.
A Practical Example of Change of Basis
Consider two bases
for a vector space
Let’s find
First, we will write our change of basis matrix,
Next, we will multiply our matrices to find the C-coordinate matrix of
Easy, right?
Case Study: Finding C-Coordinate Matrix Without B-Coordinate
But what happens if we don’t have the B-coordinate matrix?
Well, we’ll use a similar strategy of the inverse algorithm given the theorem
For example, suppose two bases
for
and the change of coordinates matrix for
First, we create our augmented matrix and row reduce so that the Identity matrix is in front and our change of basis from
So, we just found the change of coordinate matrix from B to C, or the old basis relative to the new basis, by using Row Reduction as
Now, let’s find the change of the coordinates matrix from C to B. We have two choices… we can apply the algorithm as we did above, or we can use the Invertible Matrix Theorem to our advantage, knowing that
Let’s use inverses!
Sweet!
Next Steps
In this video, you will:
- Learn how to find a new basis C
- Find the Change-of-Coordinate Matrix from
- Study the relationship between the B-Coordinate vector and the C-Coordinate vector
- Examine more examples dealing with the Change of Basis problem
- Revisit polynomials and find the Change-of-Coordinate Matrix for them
Get ready to change things up!
Video Tutorial w/ Full Lesson & Detailed Examples

Get access to all the courses and over 450 HD videos with your subscription
Monthly and Yearly Plans Available
Still wondering if CalcWorkshop is right for you?
Take a Tour and find out how a membership can take the struggle out of learning math.