Have you ever tried to peer through a dirty window? Have your glasses, sunglasses, or possibly your car windshield been so fogged up that you can’t see through? Isn’t trying to understand what’s on the other side difficult in times like this?

Jenn, Founder Calcworkshop®, 15+ Years Experience (Licensed & Certified Teacher)
As we learned in previous lessons, shifting our focus from a system of equations to vector or even matrix equations helps us better analyze the solution and provide a better view. We never actually changed the linear system; we just wrote it in such a way as to make it easier to see – we cleaned it up a bit or turned on the defrost.
However, there are other times when a simple defogging isn’t enough, and we need a bit more “umff!” and a little more action. We don’t just want to clean it up, but to truly transform it!
Matrix Equations and Transformations
The matrix equation
Connections Between Geometry and Linear Algebra
Do you remember how in geometry, we learned that transformations occur when there is a change in size, shape, or position (i.e., dilation, rotation, reflection, and translation)? Now you may wonder, how does our knowledge of geometry and transformation relate to linear algebra?
Great question! Let’s dive into it.
- Transformation is a function or mapping that takes an input and produces an output. The fascinating part is that this transformation can be expressed by a matrix and interpreted similarly.
- Confused? Let’s break it down. Just like
Matrix as Functions
Therefore,
Transformations in Linear Algebra
So, a transformation
Codomain and Range
Wait! What’s the difference between codomain and range? Aren’t they the same thing?
Well, in your previous courses, the range and the codomain probably were the same, but the distinction is quite important as you progress in mathematics. The codomain is all the possible outcomes, while the range is all the actual outcomes (images) that appear after the transformation.
So, if
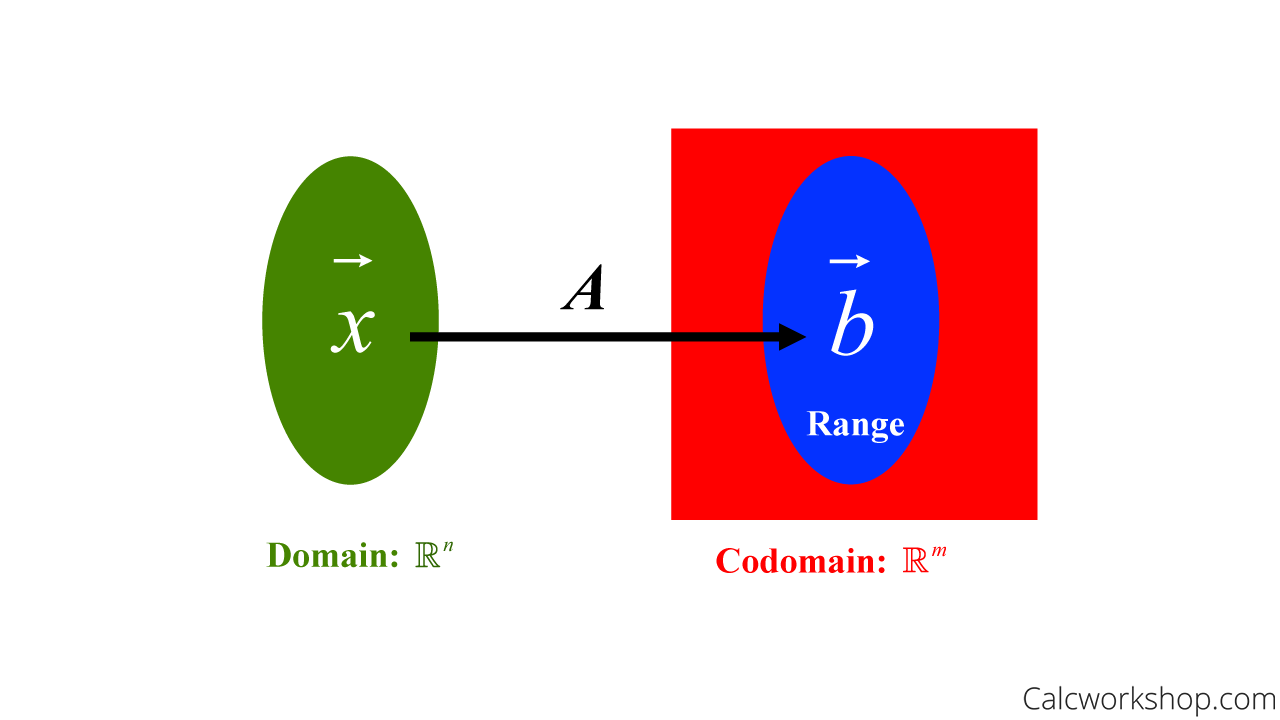
Matrix Transformation Mapping
The green oval is the input value, the red square is all the possible outcomes, and the blue oval represents the range, all the actual outputs (images) that are calculated after the transformation A.
More specifically, if A is an mxn matrix, and
- The domain of
- The codomain is the number of rows (m) of A
- The range is the column space of A
Don’t worry about understanding “column space” for now…we’ll come back to it in a future lesson, but for now, just know that the range of
Also, it may be helpful to point out that some textbooks refer to matrix A as the standard matrix for the linear transformation
One-to-One and Onto Transformations
Now it’s time to talk about one-to-one (also known as injective) and onto (also known as surjective) transformations.
For a function to be one-to-one, every distinct element in the domain has a distinct image in the codomain. All this means is that every element in the domain (the green oval from the diagram above) maps to a “unique buddy” in the codomain.
Definition: A mapping
Now, an onto function is when every element in the codomain is mapped to by at least one element in the domain. Which means nothing in the codomain is left out. Simply put, an onto function is when the range equals the codomain (the blue oval is the same as the red square)!
Definition: A mapping
Here’s a tip for keeping this straight … focus on the codomain and ask yourself how often each element gets mapped to, or as I like to say, how often each element gets “hit” or tagged.
- Injective (one-to-one): elements in the codomain get “hit” at most once
- Surjective (onto): elements in the codomain get “hit” at least once
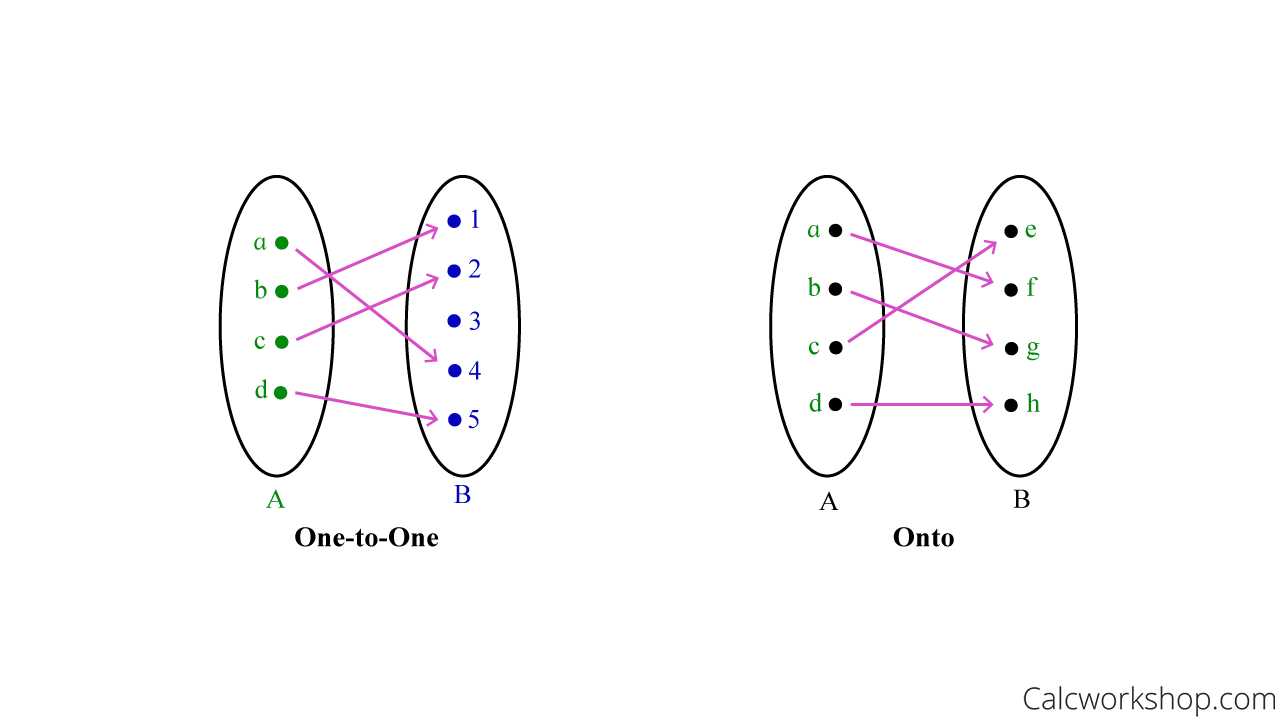
One To One vs. Onto Mapping
Matrix Transformation Theorems
We have special theorems for one-to-one matrix transformations and onto matrix transformations that will help us perform and identify linear transformations.
One-to-One Matrix Transformation Theorem: If
- For every
- For every
- The columns of
- The range of
Onto Matrix Transformation Theorem: If
- The columns of
- The range of
Linear Transformations
Okay, now that we’ve gotten all our definitions and theorems, let’s learn how to verify, identify, and compute linear and matrix transformations.
Don’t worry. You already have a leg up because of your geometry transformations (reflections, rotations, translation, and dilations).
Examples of Matrix Transformations
So, a transformation
This means that every linear transformation preserves the operations of vector addition and scalar multiplication. And why is this important? Because every linear transformation is a matrix transformation.
Moreover, a linear transformation is our formula or “action” that allows us to dilate, reflect, rotate, shear, project, and rotate, just like we did with objects in geometry!
Dilation, Reflection, and Shear Examples
Okay, so let’s look at a few examples to help us understand matrix transformations.
Example of a Dilation: If
We obtain the columns of
Example of a Reflection
Find the standard matrix A for
Just like we did for the previous example, we will be obtaining the columns of A by evaluating
When it says to reflect through the “vertical axis, ” we reflect over the y-axis. So, the
And when it says to reflect through the “horizontal axis,” that means we are reflecting over the
Example of a Shear
Find the standard matrix
Alright, so we obtain the columns of
Example of a Rotation
Find the standard matrix
Okay, so for rotations, we will use the fact that:
Therefore,
And if
Example
Show that
First, we must recognize that
See, transformations are pretty easy, right?
Next Steps
I understand this is a lot of information to process, but there’s no need to worry. You will:
- Learn all the definitions and theorems, connecting each to its geometric interpretation.
- Explore numerous examples in depth.
- Master the ability to explain, identify, and construct linear and matrix transformations!
It’s time for you to dive in!
Video Tutorial w/ Full Lesson & Detailed Examples

Get access to all the courses and over 450 HD videos with your subscription
Monthly and Yearly Plans Available
Still wondering if CalcWorkshop is right for you?
Take a Tour and find out how a membership can take the struggle out of learning math.