How to divide decimals?

Jenn, Founder Calcworkshop®, 15+ Years Experience (Licensed & Certified Teacher)
First, you need to know that there are two types of decimal division problems?
It’s true!
Some decimals are divided by whole numbers, and then some decimals are divided by decimals.
In this lesson, we’re going to learn how to do both!
Vocabulary
But first, let’s talk about some basic vocabulary and notation.
The operation of division will “undo” multiplication, as they are inverse operations of each other.
In other words, we multiply factors to find the product, and we divide the product with one of the factors to find the second factor as the example below highlights.
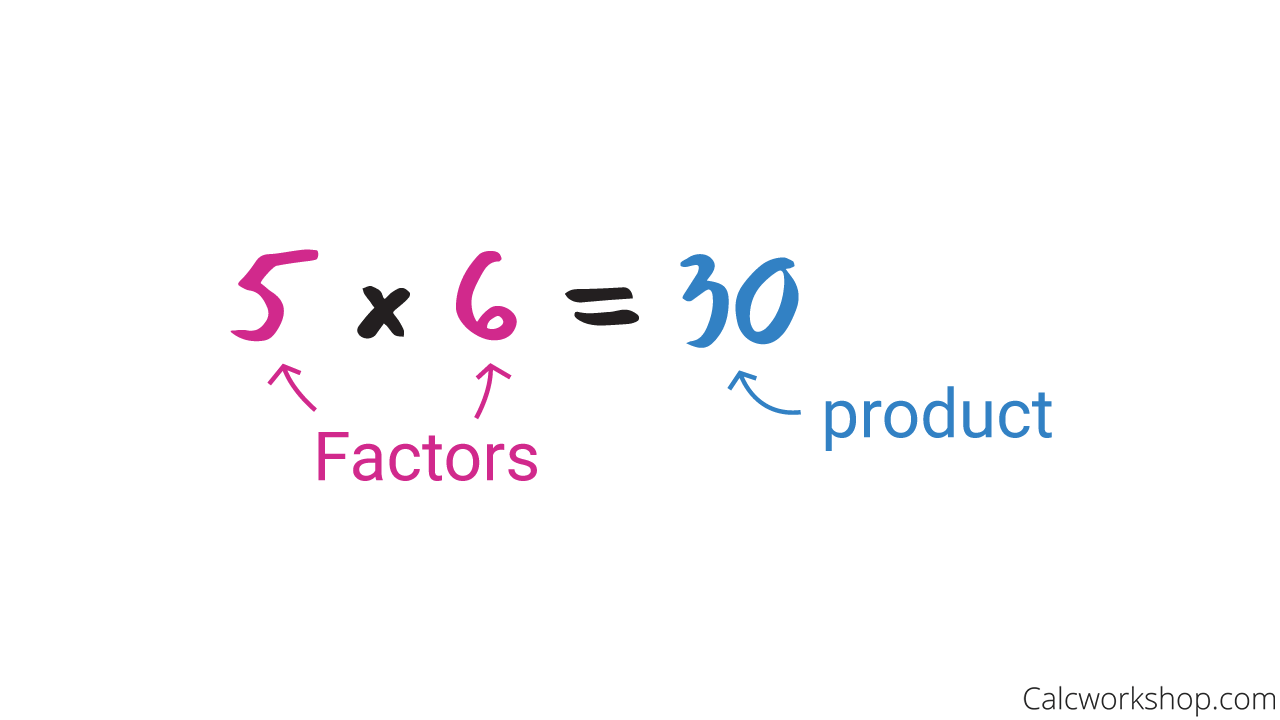
Factors And Product In Division
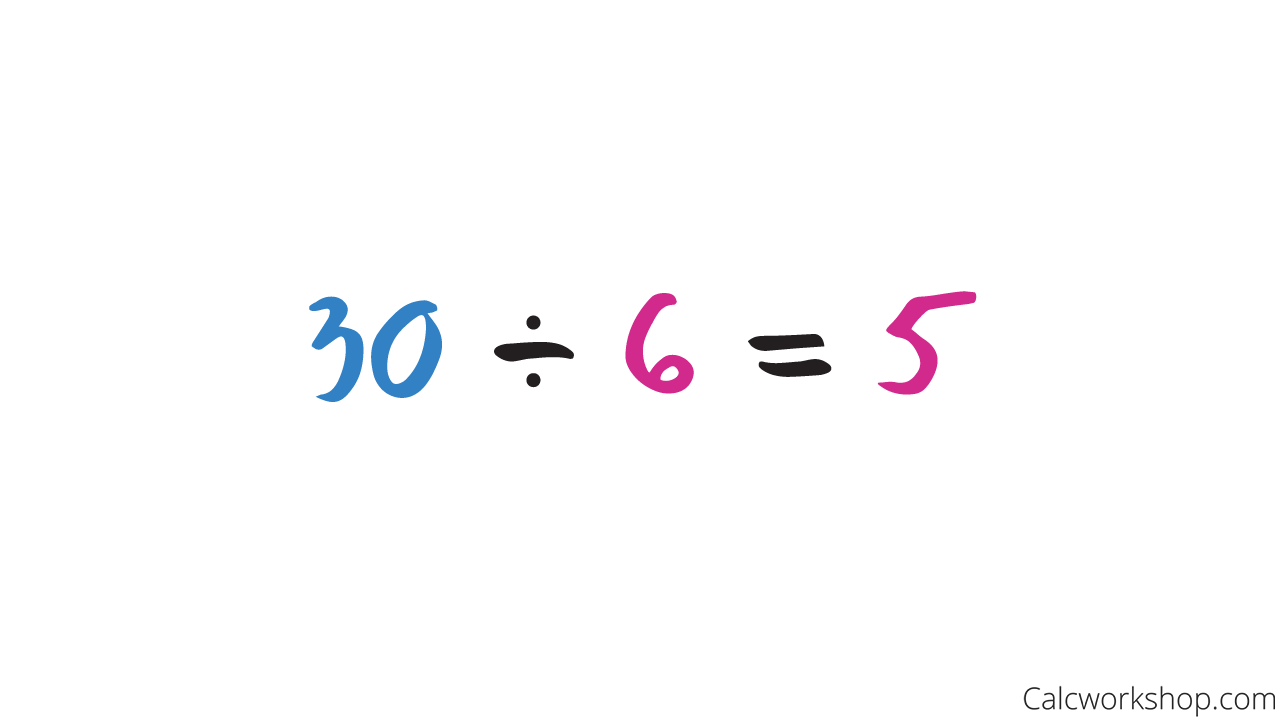
Quotient And Factor
Here’s a big HINT — they go in alphabetical order.

Dividend Divisor Quotient
Set up the long division problem by placing the dividend inside the “house” and the divisor outside the “house.”
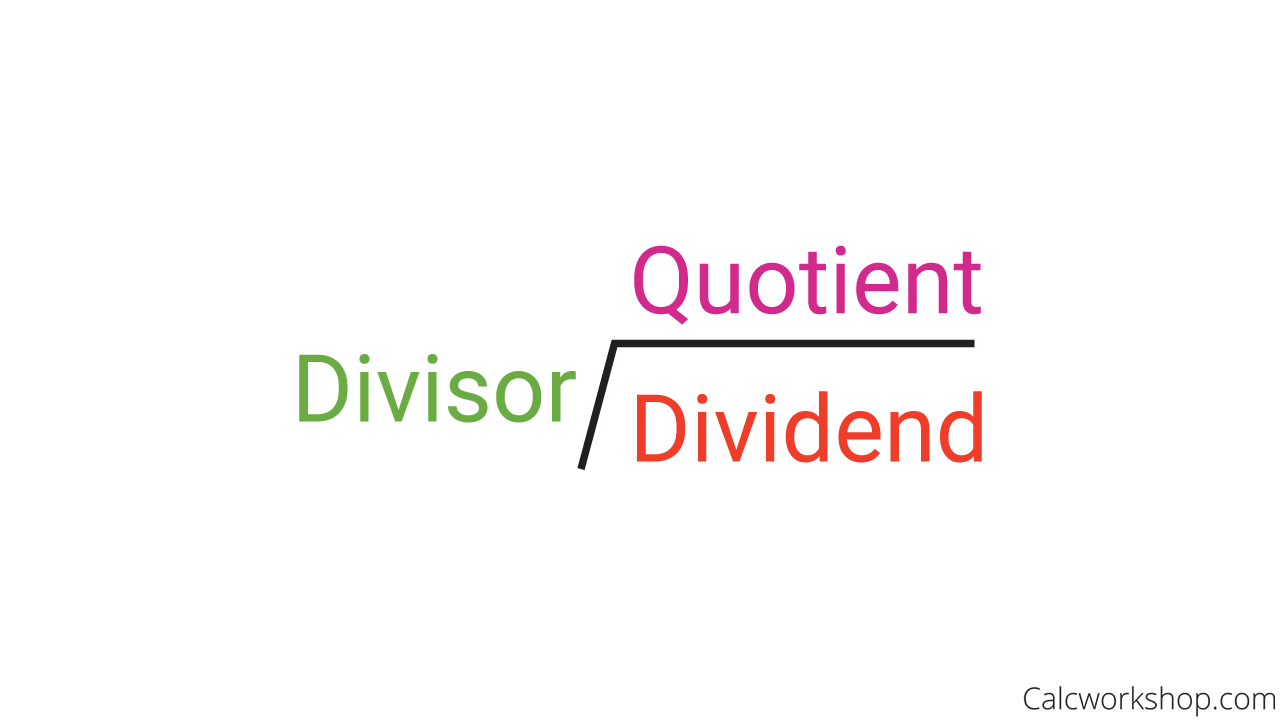
Divisor Dividend House
And now it’s time to perform the calculation. To do so, we ask ourselves, “How many times” does the divisor go into the dividend?
Then we multiply our divisor by the number that goes into the divided even or as close to it without going over and subtract it from the dividend. Then we bring down the next number and repeat the process.
In other words, we can follow these steps for long division:
- Multiply
- Subtract
- Bring Down
- Repeat
Now it’s time to talk about the two types of decimal division and the three types of answers we will find.
As previously stated, the two types of problems we will encounter when we divide decimals are:
- Whole number divisors
- Decimal divisors
How To Divide A Decimal By A Whole Number
If we have a whole number divisor, we “push” the decimal point up out of the house, as the example illustrates.
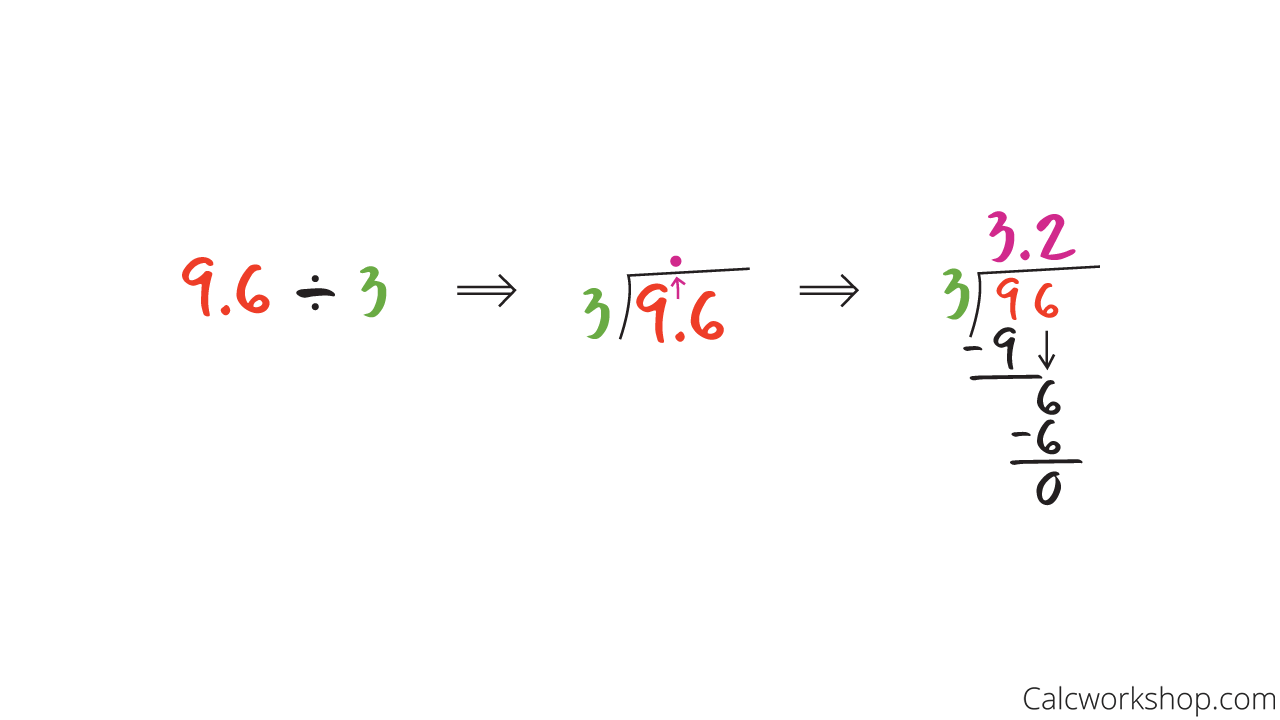
Decimal Division By Whole Number
How To Divide A Decimal By A Decimal
But if the divisor contains a decimal, then we will have to change it to a whole number.
Important fact — you can only divide when the divisor is a whole number!
So, how do we change a decimal divisor?
We multiply the divisor and the dividend by a power of ten that makes the divisor a whole number.
In other words, we move the decimal point of the divisor to the right until it creates a whole number, and we move the same number of places on the dividend as noted by Math.com. In other words, when you move the decimal point in the divisor you must also move the decimal point in the dividend.
Whatever you do to the divisor, you have to also do to the dividend!
Then we “push” the new decimal up out of the house and follow the long division steps as before to find our quotient.
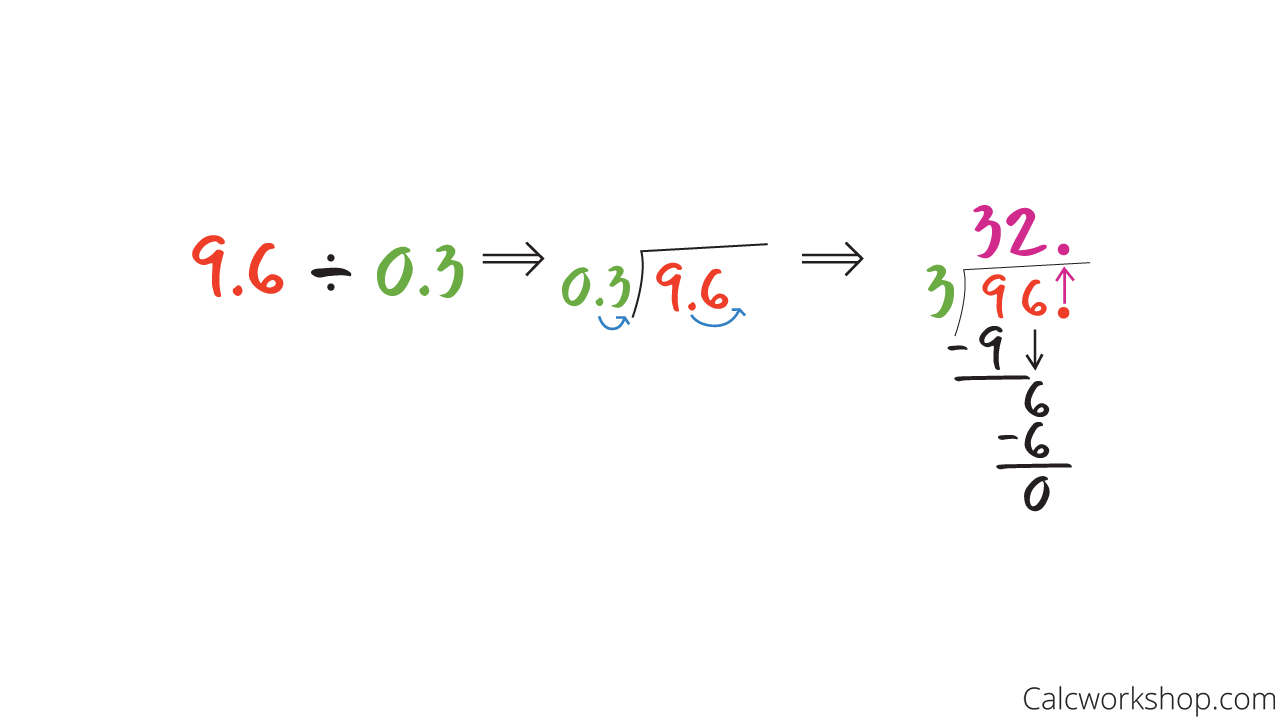
Dividing By A Decimal Divisor
But it’s important to note that we will no longer be leaving our answers with remainders. Instead, we will keep dividing, adding zero placeholders when necessary, until we find:
- A terminating decimal (remainder zero)
- Repeating decimal
- Or a decimal that does not terminate or may terminate but is just impractical to find
When we encounter this third type of situation, we will usually stop once we have gone 4 or 5 places after the decimal point.
5th Grade Division
Typically, decimal division is first discussed in grade 5, where you will be asked to use only whole number divisors or very simply base-ten decimal divisors.
6th, 7th, and 8th Grade Division
In grades 6 and 7 and even grade 8, you will be working with both whole number and decimal divisors and applying those skills to multi-digit decimals.
Solved Examples
Okay, so let’s look at a few examples.
Terminating Decimal
This first example is when we divide by a whole number (i.e., whole number divisor) with a terminating answer.
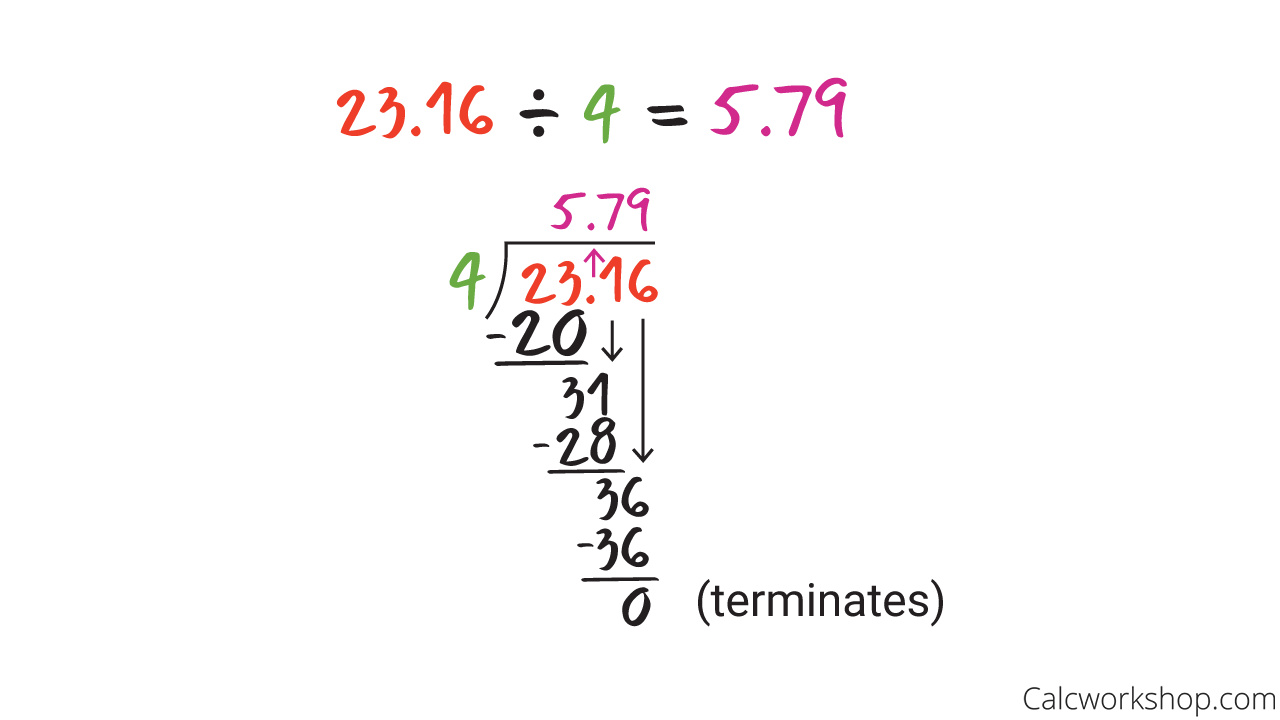
How To Divide A Decimal By A Whole Number
Repeating Decimal
Our second example deals with a decimal divisor (i.e., having to move the decimal place) with a repeating answer.
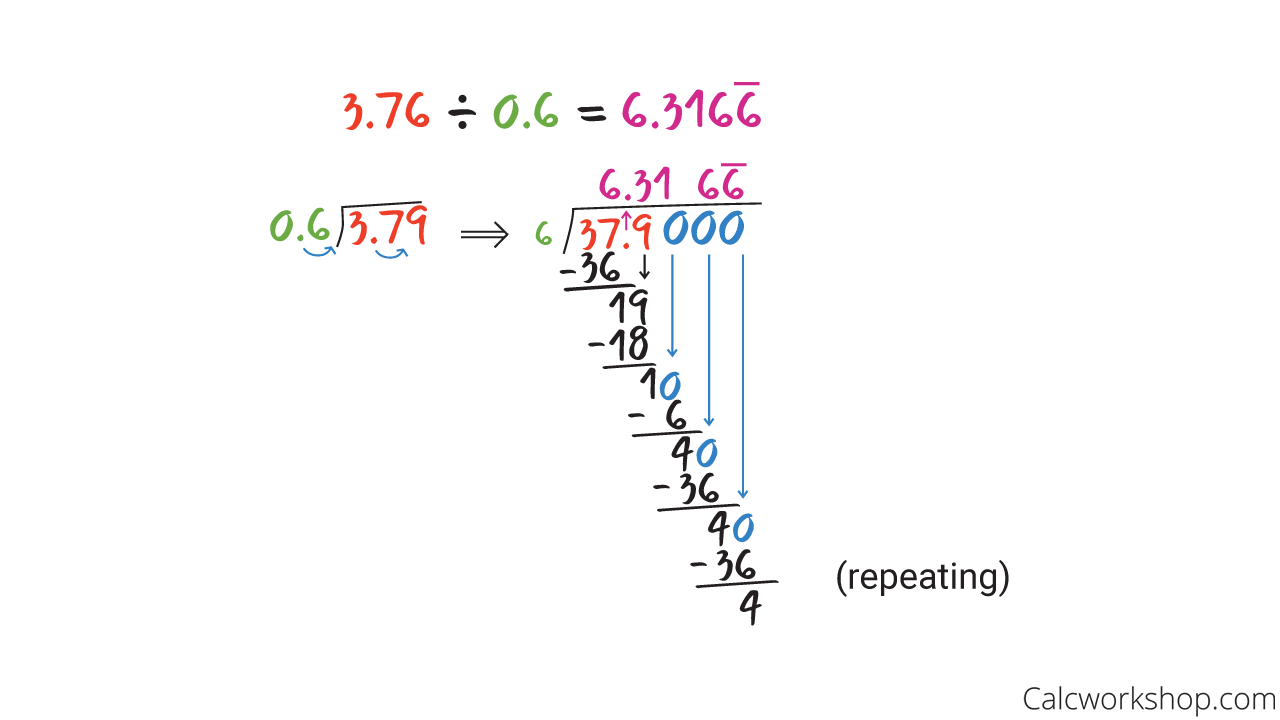
How Do You Divide By A Decimal
Non Repeating Decimal
And our third example also deals with a decimal divisor but with a non-terminating and non-repeating answer.
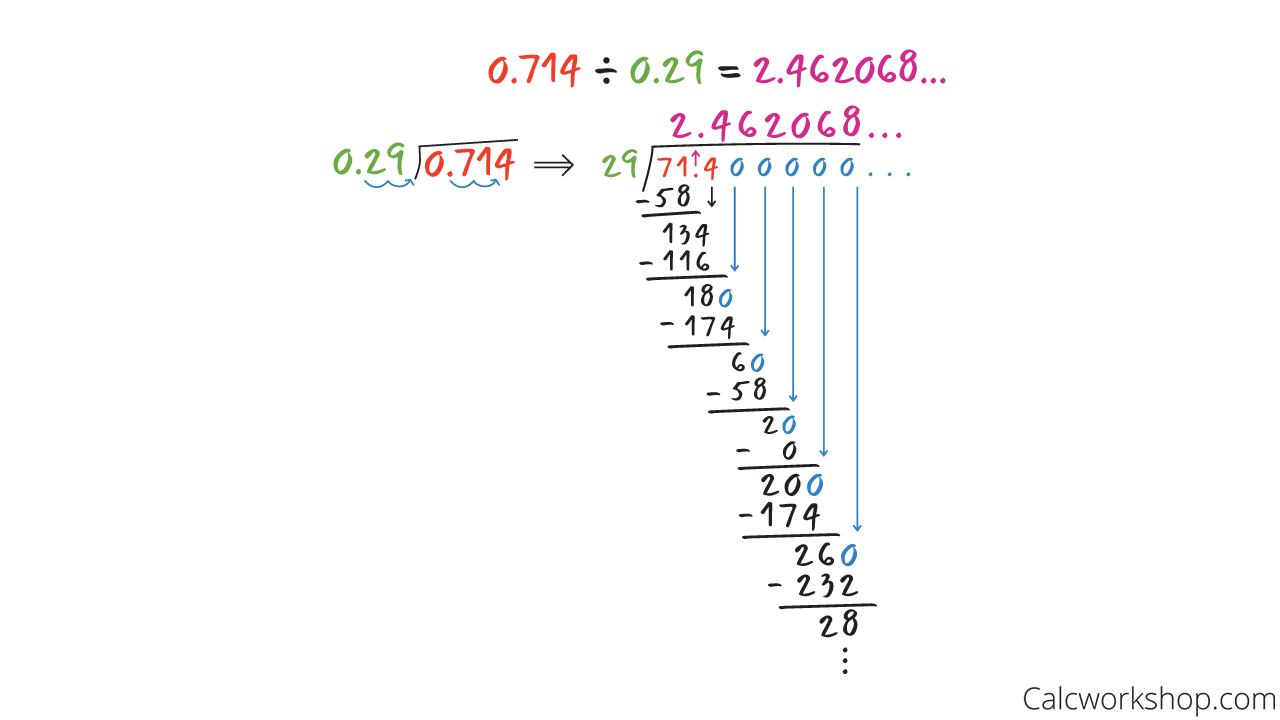
Dividing by a Decimal Divisor (Non-Terminating)
We will work through numerous examples, just like the ones seen above, pointing out tricks along the way so that you will feel comfortable solving any decimal division problem.
Worksheet (PDF) — Hands on Practice
Put that pencil to paper in these easy to follow worksheets — expand your knowledge!
Practice Problems
Step-by-Step Solutions
Division Words
We will also look at some keywords and phrases that indicate “division,” like:
- Quotient
- Split
- Ratio
- Half
- Quarter
- Etc.
And discuss how division is not commutative because order matters. Meaning, if you switch the dividend and divisor, you will get very different answers.
Alright, let’s jump right in!
Dividing Decimals – Lesson & Examples (Video)
1 hr 4 min
- Introduction to Video: Dividing Decimals
- 00:00:38 – How to identify the dividend, divisor and quotient
- 00:06:30 – What are the two types of decimal division? And what are the three types of answers for dividing decimals
- 00:10:34 – Divide the decimal by a whole number (Examples #1-2)
- 00:16:02 – Find the quotient using zero placeholders (Examples #3-4)
- 00:21:13 – How do you divide a decimal by a decimal?
- 00:23:27 – Divide the decimal by a decimal divisor (Examples #5-6)
- 00:28:16 – Divide by a decimal divisor and find either terminating or repeating answers (Examples #7-10)
- 00:44:39 – Find the quotient (Examples #11-14)
- 00:59:18 – What key words indicate division? Is division commutative?
- Practice Problems with Step-by-Step Solutions
- Chapter Tests with Video Solutions
Get access to all the courses and over 450 HD videos with your subscription
Monthly and Yearly Plans Available
Still wondering if CalcWorkshop is right for you?
Take a Tour and find out how a membership can take the struggle out of learning math.