Classifying triangles is an essential skill when starting out in your geometry course.

Jenn, Founder Calcworkshop®, 15+ Years Experience (Licensed & Certified Teacher)
In today’s lesson we’re going learn how to classify the various types of triangles.
Review the triangle sum and exterior angle theorems, and finish up with two column proofs.
Here we go!
What is a triangle?
A triangle is formed by three segments that join three noncollinear points.
Each segment is called a side of the triangle and the point where two sides meet is called a vertex.
How do we classify a triangle?
Are there different types of triangles?
Yes, triangles come in different shapes and sizes and we distinguish dissimilar triangles by either their sides or angles.
1. Classifying Triangles by Sides
We can classify triangles according to the measure of their sides. In the figures below, sides are marked to show which are congruent. In a scalene triangle all three sides have different measures, therefore a scalene triangle does not have any congruent sides. An isosceles triangle has two sides that have the exact same measure. And a triangle where all three sides have the same measure is called an equilateral triangle. And every equilateral triangle is also an isosceles triangle, since it has two sides that are congruent.
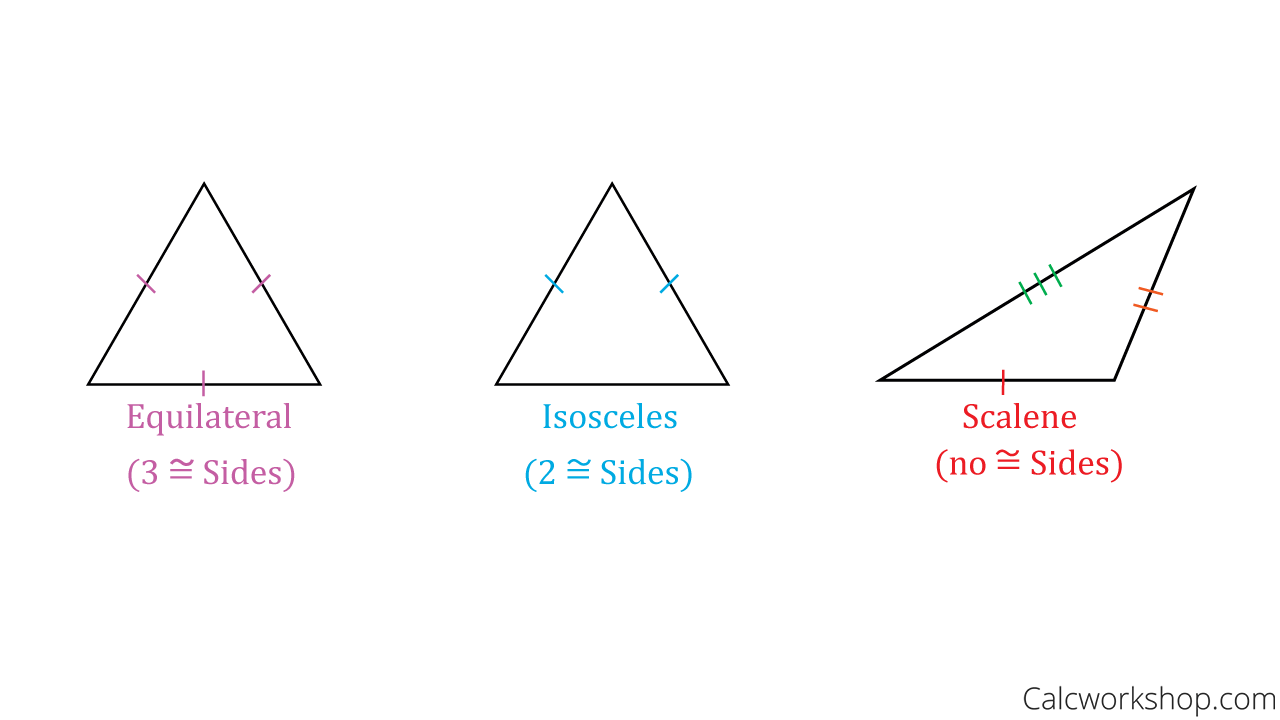
Classifying Triangles by Sides
2. Classifying Triangles by Angles
Triangles can also be classified by their angles. In an acute triangle all three angles are acute (less than 90 degrees). A right triangle contains one right angle and two acute angles. And an obtuse triangle contains one obtuse angle (greater than 90 degrees) and two acute angles. And an isosceles triangle has two congruent angles. Additionally, an equilateral triangle not only has three congruent sides, but also three congruent angles all measuring 60 degrees. Likewise, an equilateral triangle is also an acute triangle.
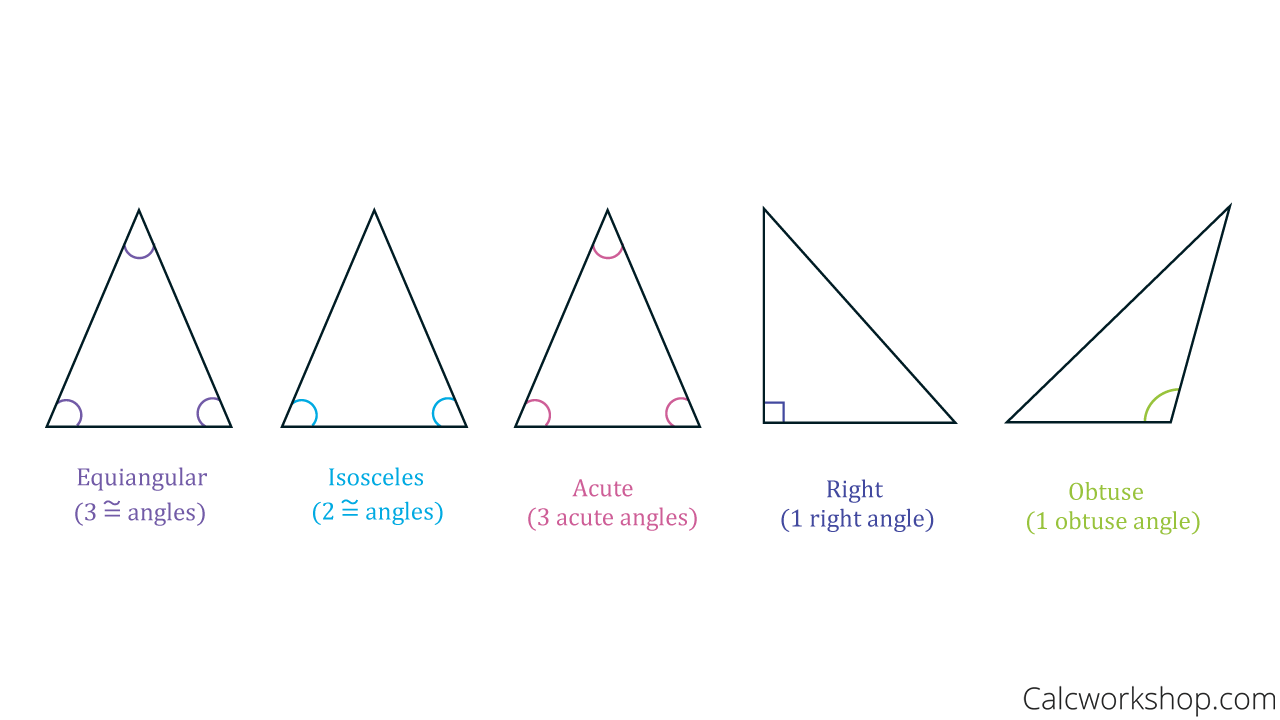
Classifying Triangles by Angles
In addition, we can find angle measures for both the interior and exterior angles with the Triangle Sum Theorem and the Exterior Angle Theorem.
The Triangle Sum Theorem, also referred to as the Angle Sum Theorem, as Online Math Learning accurately states, says that the sum of the measures of the three interior angles in a triangle is always 180°.
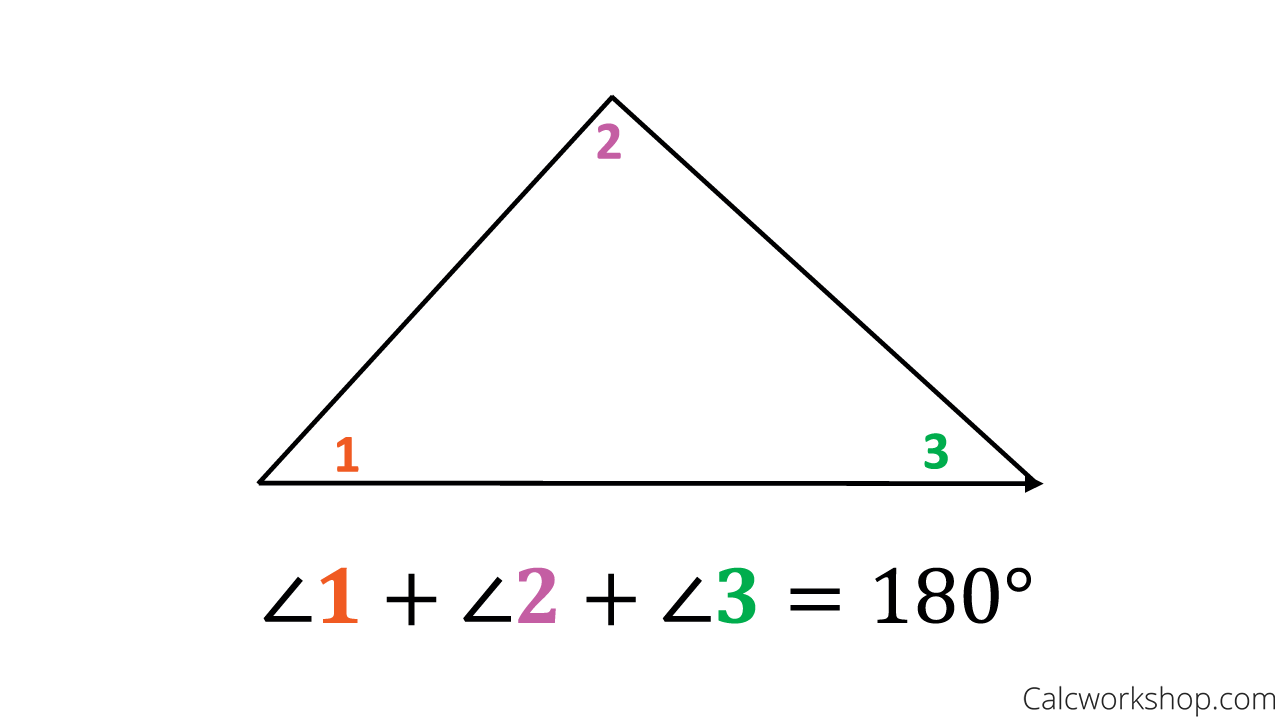
The sum of the interior angles in a triangle always equals 180 degrees.
The Exterior Angle Theorem tells us that the measure of an exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of the measures of the two nonadjacent angles (sometimes called remote interior angles).
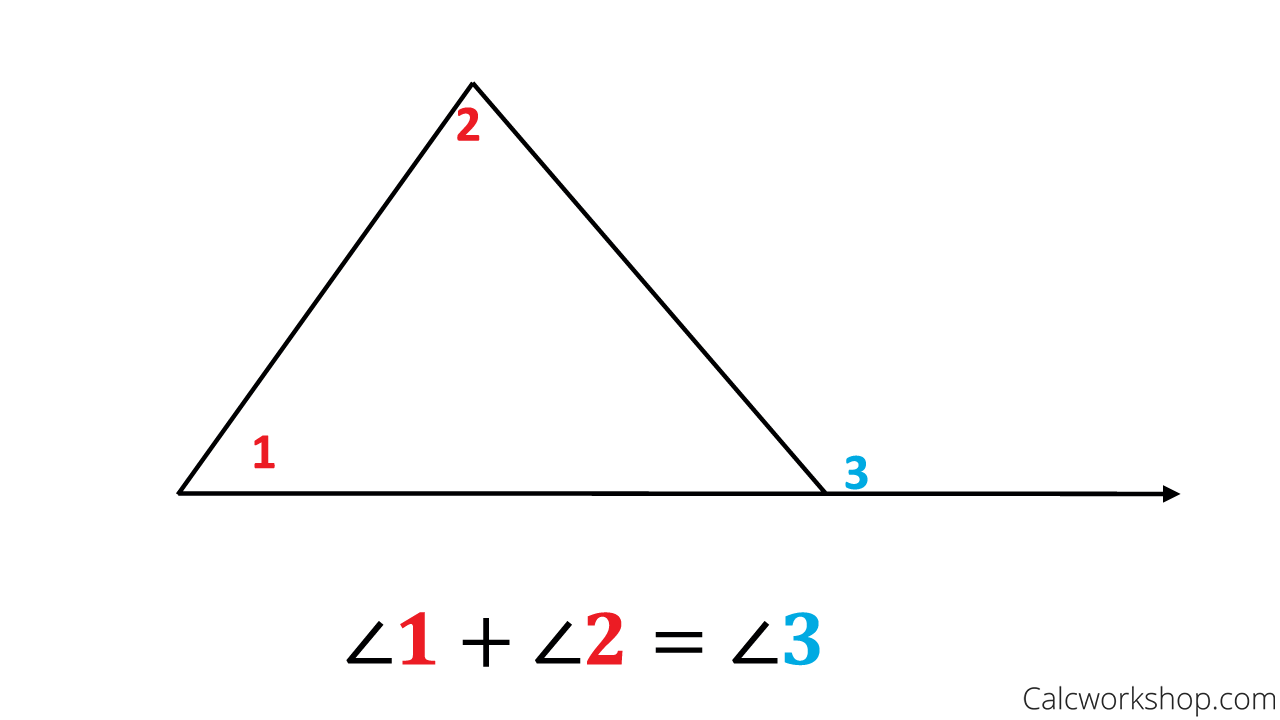
The sum of the non adjacent angles in a triangle equals the exterior angle
This means that if we know two angles measures for a triangle, we can find the third!
And if we create a triangle between two parallel lines, then we can also apply our knowledge of angle-pair relationships such as the congruence of corresponding angles and alternate interior angles.
Sweet!
In this video lesson, we’ll look at:
- How we classify triangles.
- Prove the triangle sum theorem.
- Use our new theorems and postulates to find missing angle measures for various triangles.
- And we’ll even tackle a two column proof.
Classifying Triangles – Lesson & Examples (Video)
51 min
- Introduction to classifying triangles
- 00:00:30 – How do we classify triangles? Overview of the types of classification
- 00:08:05 – Identify the type for each triangle (Examples #1-11)
- Exclusive Content for Member’s Only
- 00:20:45 – What is the triangle sum theorem and the exterior angle theorem?
- 00:28:57 – Find the degree measure of each angle in the triangle (Examples #12-14)
- 00:41:15 – How to find the measure of an angle in a triangle (Example #15)
- 00:45:45 – Complete the two column proof (Example #16)
- Practice Problems with Step-by-Step Solutions
- Chapter Tests with Video Solutions
Get access to all the courses and over 450 HD videos with your subscription
Monthly and Yearly Plans Available
Still wondering if CalcWorkshop is right for you?
Take a Tour and find out how a membership can take the struggle out of learning math.