The demand for certain products are sensitive to any change in price, and being able to determine how changing prices will affect revenue is called Price Elasticity of Demand, or Demand Elasticity.

Jenn, Founder Calcworkshop®, 15+ Years Experience (Licensed & Certified Teacher)
For items or products that people have deem essential, like bread or milk, tends to be what we call Inelastic. Even if the price goes up, people are still going to buy it.
Whereas, items that people consider a luxury, like cars or new clothes, tend to be Elastic. If the price goes up, people will either not buy or can do without or put off until later, thus causing revenue to drop.
So how do we best determine whether or not to increase or decrease prices in order to increase Revenue?
The Elasticity of Demand Formula.
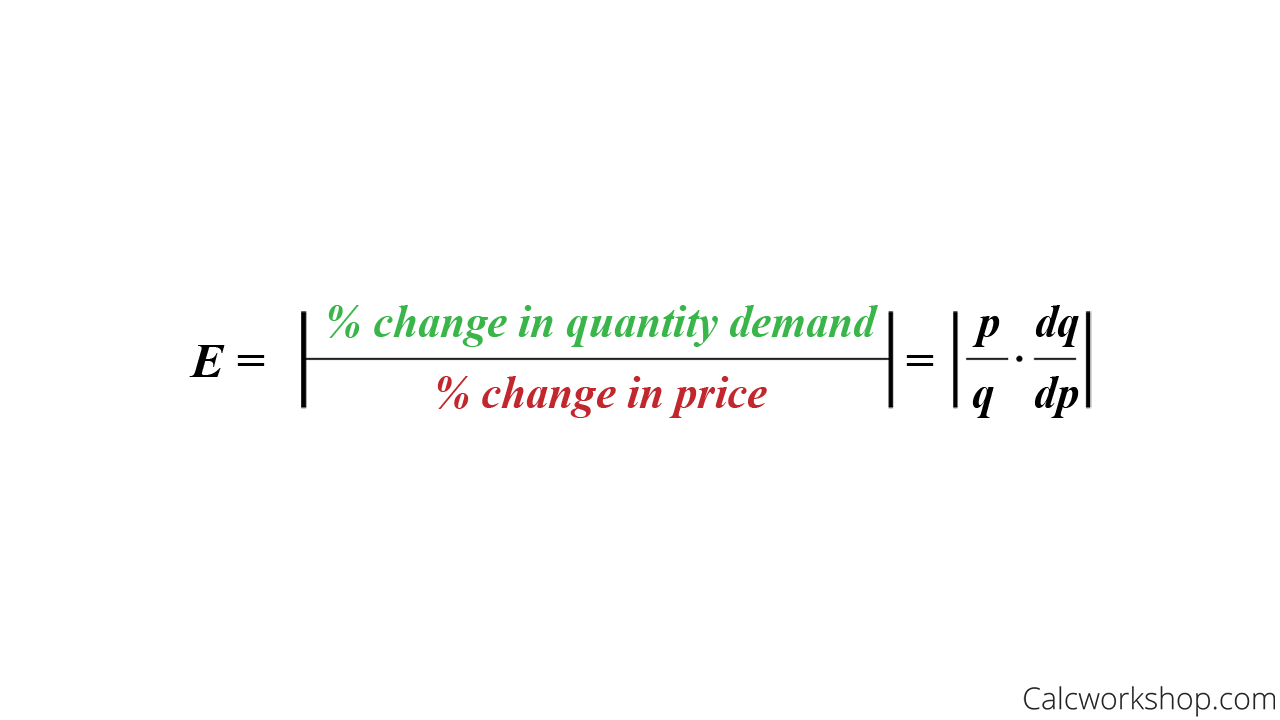
Price Elasticity of Demand
The formula for Elasticity measures how demand reacts to price changes. This means the particular prices and quantities don’t matter, and everything is treated as a percent change, as Grove City College accurately states.
In other words, if the price increases by 1%, the demand will decrease by E%.
Together we will look at five examples in detail, and learn how to determine if raising prices will increase or decrease revenue.
Elasticity of Demand – Video

Get access to all the courses and over 450 HD videos with your subscription
Monthly and Yearly Plans Available
I'm in school to get my degree Networking and Cybersecurity and I'm in my first year. I've been away from school for quite a long time so the concepts that are being taught although not foreign to me, have so much dust on them from a lack of being used in real world applications regularly.I stumbled upon CalcWorkshop by pure chance and it has been a game changer for me. Jen filled in the gaps in between what my Professor is teaching at a rapid fire pace and where my brain grasps and applies it. If not for Jen's approach, I'd have failed my test I took miserably!Am I grateful? It goes beyond words and not I recommend her workshops to everyone!
I got calc workshop because my teacher wasn't doing a good job of teaching calculus 3 to me, but after months of banging my head against the wall trying to understand my assignments, I finally decided to give calc workshop a try, and it was amazing. I felt like I finally understood what I was supposed to be learning
Very happy with the product!
CalcWorkshop, is truly amazing. You can find almost all of the math courses and everything is explained in detail. You'll also find notes and practice tests for each chapter. I really love it, affordable price and you can cancel anytime. I will definitely recommend friends and family. Thank you, Jenn for sharing your knowledge and skills. Highly appreciated!
I absolutely love Jenn! She is a fantastic teacher!!
I absolutely love this subscription. At first I was iffy about spending the money, but in the long term it is so worth it. I started watching Jenn almost 3/4ths into my calc 2 class, and I a confidently say I understand the depths to each topic. Before, with my professor I felt that I only understood surface level of each topic. But after the CalcWorkshop videos, I have acronyms, tips, and knowledge I walk away with, that I didn't have before. Genuinely cannot wait to keep using this website for my future endeavors, minoring in Mathematics!
The best resource for improving my math skills and improving my performance in Calculus, as well as through other areas that pertain to other math courses! Jenn is an incredible teacher and I recommend Calcworkshop to anyone who experiences insecurity in math.
My experience was great! I needed help studying for my math class, but I wasn't sure how-until an ad for this popped up on my YouTube. After watching the ad, I was convinced, so I subscribed to CalcWoskop. I'm so happy I did because it helped me so much with my class! I learned a lot that I couldn't grasp from my college lectures, and this was the perfect solution.
I had an Amazing experience with discrete math and calculus series. Graduating with highest honors thanks to calc workshop. I'll be back on the site again but this time if I need to go back as reference as well as if I get rusty in my career.
I found Jenn's videos near the end of my discrete math class, so I only had a month to go through all of her discrete math lessons to study for my exam. I'm sure I would have aced it if I had more time but I got a pretty good grade considering I thought I would fail.So happy to be done that class!As advertised, Jenn is very thorough and doesn't skip steps, she lets you know exactly how she gets from a to b or she will refer you to other videos where she teaches the techniques she's using more in depth. This was extremely valuable to me, being a mature student taking advanced math while not remembering basic algebra.And it was fun to understand and solve complex problems vs memorize proof structures.
Very well organized, helpful and comprehensive. It is great also to have access to prior course material so you can easily go back and refresh if you need to. Jenn is very clear and the number of examples leaves one comfortable with each topic. Couldn't be happier.
I had to take Calculus I and II as accelerated classes while working full time. It was my first time taking this courses and was very overwhelming. Calcworkshop really made learning the subjects easier for me by having all the subjects easy to find and easy to understand explanations. I received a B in both classes which I am extremely happy with doing the classes in double time.
Jenn is awesome!Her breakdown of the topic is beyond what you would expect. She is showing you how to arrive at the answer instead of doing a simple equation. Most people need to know the why it give confidence and structure to the learning process. This is what Jenn is great at, she knows how to deliver the information to a non math mind in a way that instills knowledge that you can forever draw from as you move forward. It's really well thought out. She is a true master teacher. Thanks for all that you do for us! Hugs n Blessings... JS
Best instructor ever, I have never had Math explained in a way that was so interesting. Her lectures and instruction is explained perfectly, and I will continue to use this for all my future math courses.
I needed help with college precalculus, they provided more than enough help that allowed me to succeed and get the scores I needed.
I love the videos the way each lesson is explained step by step. I love that she has examples that you can go over again and again in order to understand the way algebra works. I was lost because my instructor was flying through each lesson and I was totally lost. I attached my syllabus and they helped me stay focus on what I was working and give me a guide to go back and refresh what I went over in class.
I am 47 years old and a freshman in college. I started studying with Jenn at calcworkshop a few months before my first semester and during. I am proud to say I achieved a 4.0 GPA and a spot on the Dean's list. Thank you so much! Great learning tool here!!!
I could not recommend calcworkshop enough; the style and format Jen instructs in is amongst the best I have seen, and I would not have made it through my mathematical journey without her. I recommend this website to anyone who ever confides in me that they are having troubles in any math class, not just calculus. Forever grateful!
The videos were extremely helpful! Thanks so much for explaining everything in detail!
I started w/Jenn because I love math and have a reading handicap. I am very happy to start from the beginning again with her help and guidance. I can tell Jenn loves math as much as I do and she is willing to teach the beginning with as much zeal as the advanced.
My experience has been great so far! I purchased this because I got frustrated searching YouTube for how to information. It is affordable, great supplemental information to my course!
Jenn at calc workshop did such a good job breaking all of the topics down that were still nebulous to me after agonizing over them in lecture. I actually started to enjoy calculus the less I felt overwhelmed by it-she's a lifesaver!
My daughter has started using this platform and finds the lessons absolutely fantastic to gain a deeper understanding of the topics.
Video's are great and easy to understand. Examples are very helpful. These are all the topics needed for a college level Calculus course.Very useful for courses that are taught in a room with 100 people and you cannot get the 1:1 help
As an older student years removed from Calculus going back to school Jenn does a very good job refreshing prior theories from Geometry or Algebra II.
Calc workshop is an amazing service which helps struggling students with their math work.
Hello, I highly recommend getting a subscription to Jenn and her Calcworkshop teaching math service. I did a general, "go from bad to good at math", Google search and found out about Calcworkshop through responses to the topic on reddit. I've just started watching her videos and found them to be extremely helpful. I'm going back to college after a long absence and math was never my strong suit. So I'm starting at the very bottom of her available subjects and going from there. Just watching a couple of the videos has taken me from being dragged along not understanding to following along just fine in my math class. I'm moving from the "I'll never get this", to the "I look forward to understanding this", mindset in approaching math. This for me is huge, and even though I have a long way to go, I'm confident I will get there thanks to Jenn. Totally worth it!
Very thorough, great examples, great explanations, pleasant demeanor, great resource.
My only problem with Calc Workshop was that I ended up buying it too late in the semester! Jenn's videos are super great, and all of the practice problems definitely helped me more than I thought it would. The next time I sign up for a math class, I'm signing up for Calc Workshop again, too!!
Very helpful and nicely paced. Definitely turned my failing stats grade to passing
Best math videos out there without a doubt! thanks for helping me in several courses throughout college.
This website has everything you need to succeed in school. Jenn is a terrific teacher, she breaks down everything in a way that even without a solid mathematical foundation, you would be able to understand!
I only wish I have signed up sooner. The way in which the instructions are provided are perfect. I was struggling with my work, with having school tutor. But the way she explains things are such that makes sense. Additionally the workshop exercises are an additional resource. Certainly recommend the site! Thanks.
I have only had it for a few weeks now but it has been very very helpful in getting me back up to where my other classmates stand in my pre calculus class thank you very much!
Calcworkshop is an outstanding source to learn math and understanding math concepts. Jenn is an outstanding master teacher. Every lesson is clearly presented making understanding easy to grasp. Practice lessons with accompanying answers are given for each section. I am 82, a retired teacher and lifelong learner. Learning calculus has always been on my bucket list. Calcworkshop is helping me reach my goal.
Calc workshop is the absolutely best resource for math and I have seen almost everything that exists out there. I have even recommended it to my daughter's school so that all the kids could use the videos during the summer months for the subject they plan to study in the fall. They are guaranteed to get a A if they have watched the videos and completed the problems before taking the class. Students who are weak in areas can access lower level classes and those who seek to advance above grade level can do so. The videos and exercises are crystal clear and the excellent presentations raise the bar for teachers everywhere. I have always believed that one great math teacher is important in the education process. The videos, exercises and problems are excellent. It is not possible to have ANY knowledge gaps. I have never seen anything on the market that even begins to compete with it!
Calc workshop is amazing. Jenn goes a great job of breaking down everything into bite-sized pieces. She's the reason that I passed Calculus II and graduated. My only regret is that I didn't find this earlier in my college career.
Calculus can be a scary subject. I know I was scared. I had been out of any math class for over 23 years. I had taken an 8 week Calculus 1 class and felt like I was overloaded. Going into Calculus 2 I found CALCWORKSHOP.com. I used the training videos and material to really dive back into Calc 1 and prepare for Calc 2. Long story short with the material provided and ample study time, I finished Calc 2 with a 95%. Thanks Jenn!
Jenn's videos were life changing for me and my journey through Calculus 1-4 and linear algebra. I wish I would have found her videos earlier. I always struggled with math until I watched her videos. I don't know if I would have made it through all my college math classes with out her helpful videos!
Amazing, Calc workshop helped me pass Calc 1 and 2 in college.
Great site! Phenomenal understanding of high level math and how to teach it.
calcworkshop.com has been a phenomenal experience! Difficult subject matter is explained clearly and I felt I learned it better than in class.
I decided to subscribe about 12 weeks into the 16 week Calculus I class. So far it has helped tremendously. I wish I had signed up at week 1. I look forward to learning with Jenn and the Calcworkshop for future classes.Thank you, Jenn!Regards,Frank
CalcWorkshop was a wonderful resource as someone going onto a college calculus 1 class after not having taken a math course in a year! Jenn always explained things in a logical order that built upon previous lessons, and the way she explained topics was always easy to understand. Calcworkshop saved this semester for me, and I couldn't be more grateful to have found this site. :)
Anyone struggling with math at any level would greatly benefit from this product. I signed up for it immediately after getting a D on my first exam in calculus 2 and ended up getting A's and B's on the remaining exams, getting a B overall in the class. Jenn breaks down the topics, without skipping any steps, in a way that makes them very easy to understand. I highly recommend this product!
Amazing website. I've passed calculus 2 and 3. I went from barley passing to passing with an A. I didn't need to take my final exam because my grades were good enough.
Great site for (re-) learning mat at any level. Especially good for those that like a "lecture format" and have examples worked as you learn. Perfect level of detail and if something is very familiar, you can just jump ahead.
I truly don't think I would have passed my Calc 1 class if it wasn't for Calc Workshop! Truly one of the best resources to take advantage! Don't wait; start your Calc Workshop journey now and you'll do great!!
I have been using Calcworkshop for a couple of weeks now, and I do like the videos, explainations and the practice so far. I need to put in the time and Jenn at Calcworkshop has the material that I can use to practice with.-David
The only negative about this website is that I subscribe to it 3/4 of the way into my semester when I should've done this at the beginning of the semester she has helped so much and I'm really trying to pass my course as my professor is not really any help!
I'm in school to get my degree Networking and Cybersecurity and I'm in my first year. I've been away from school for quite a long time so the concepts that are being taught although not foreign to me, have so much dust on them from a lack of being used in real world applications regularly.I stumbled upon CalcWorkshop by pure chance and it has been a game changer for me. Jen filled in the gaps in between what my Professor is teaching at a rapid fire pace and where my brain grasps and applies it. If not for Jen's approach, I'd have failed my test I took miserably!Am I grateful? It goes beyond words and not I recommend her workshops to everyone!
I got calc workshop because my teacher wasn't doing a good job of teaching calculus 3 to me, but after months of banging my head against the wall trying to understand my assignments, I finally decided to give calc workshop a try, and it was amazing. I felt like I finally understood what I was supposed to be learning
Very happy with the product!
CalcWorkshop, is truly amazing. You can find almost all of the math courses and everything is explained in detail. You'll also find notes and practice tests for each chapter. I really love it, affordable price and you can cancel anytime. I will definitely recommend friends and family. Thank you, Jenn for sharing your knowledge and skills. Highly appreciated!
I absolutely love Jenn! She is a fantastic teacher!!
I absolutely love this subscription. At first I was iffy about spending the money, but in the long term it is so worth it. I started watching Jenn almost 3/4ths into my calc 2 class, and I a confidently say I understand the depths to each topic. Before, with my professor I felt that I only understood surface level of each topic. But after the CalcWorkshop videos, I have acronyms, tips, and knowledge I walk away with, that I didn't have before. Genuinely cannot wait to keep using this website for my future endeavors, minoring in Mathematics!
The best resource for improving my math skills and improving my performance in Calculus, as well as through other areas that pertain to other math courses! Jenn is an incredible teacher and I recommend Calcworkshop to anyone who experiences insecurity in math.
My experience was great! I needed help studying for my math class, but I wasn't sure how-until an ad for this popped up on my YouTube. After watching the ad, I was convinced, so I subscribed to CalcWoskop. I'm so happy I did because it helped me so much with my class! I learned a lot that I couldn't grasp from my college lectures, and this was the perfect solution.
I had an Amazing experience with discrete math and calculus series. Graduating with highest honors thanks to calc workshop. I'll be back on the site again but this time if I need to go back as reference as well as if I get rusty in my career.
I found Jenn's videos near the end of my discrete math class, so I only had a month to go through all of her discrete math lessons to study for my exam. I'm sure I would have aced it if I had more time but I got a pretty good grade considering I thought I would fail.So happy to be done that class!As advertised, Jenn is very thorough and doesn't skip steps, she lets you know exactly how she gets from a to b or she will refer you to other videos where she teaches the techniques she's using more in depth. This was extremely valuable to me, being a mature student taking advanced math while not remembering basic algebra.And it was fun to understand and solve complex problems vs memorize proof structures.